Reproduction of flowers at home - several effective ways
Flower propagation at home is often necessary for flower growers, and they do it for different purposes:
- Increasing the number and variety of available plants
- Rejuvenation of old bushes
- Saving a sick flower
- Replenishment of your collection with a new, spectacular item
- For gift and for sale
Existing breeding methods allow you to grow a beautiful flower yourself and not buy it in a store. In most cases, breeding will not require additional equipment. It is necessary to prepare large and small containers, pots, earthen mixture, preparations for rooting and growth stimulation, a sharp knife.
The main method of reproduction of indoor plants is vegetative, also called asexual, because it does not require pollination. The ready-made shoots created by the plant are used or parts of the stem or leaves are grown. It allows you to preserve all the qualities and characteristics of the parent flower. The process is simple, fast and reliable.
Propagation by cuttings
The vegetative propagation method is the most common. A stalk is a viable part of a plant that can take root.
Cuttings are of various types:
Apical
Stem
Median
Leafy
Each type of home flower can be propagated by one or more types of cuttings.
Suitable for ampel colors and.
The apical shoot is obtained from the upper, not lignified sections of the stem. He should also have 3-4 full sheets. A cut on the shoot is made under the knot, retreating 1 cm. It is on the knot that new roots will first appear. It is desirable to treat the cut with a growth stimulant. The cuttings are placed in a moist and loose rooting substrate and covered with foil.
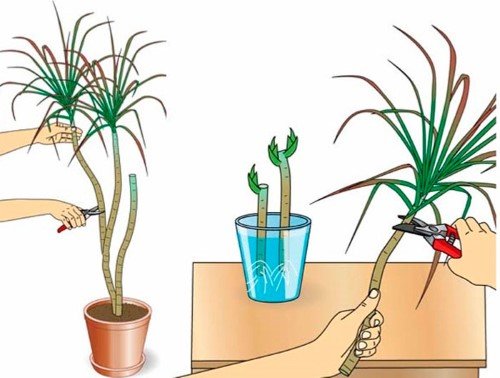
In this way, succulents, ficuses and geraniums multiply.
The stem cutting is cut from the mother plant below the node. It should not have flowers or buds. The lower leaves are removed. Rooting of the sprout is carried out in garden soil with the addition of large quantities of sand. After the roots grow back, which will happen after 3-4 weeks, the seedling is placed in the main pot.
Rooting successfully takes place in a glass jar of water.
Succulent shoots are dried for 2-3 days before planting in the soil. The place of the cut should be covered with a film, which will exclude decay. The planted cuttings are not watered, but slightly moistened by spraying.
Succulents and geraniums do not need greenhouse conditions for rooting. The rest of the plants are covered with foil or glass to maintain moisture.
The container is placed in a bright place away from sunlight. Cuttings are carried out during the active growing season in spring and summer. Fuchsia and geranium take root better in late summer. The middle cut is obtained from a part of the stem by cutting it at the bottom and middle of the shoot. In this way, it multiplies, for example,.
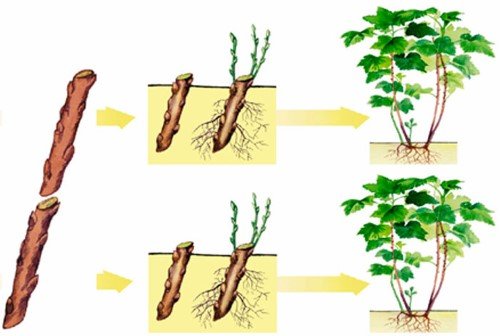
Leafy cuttings
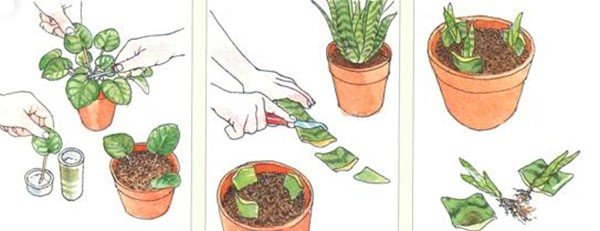
Leaf cuttings are carried out for saintpaulias or, bush begonias, gloxinias. For reproduction, Saintpaulia and Gloxinia take a strong leaf, without being affected by diseases. Cut so that a long stalk remains. It is placed in loose soil until a daughter plant emerges from the ground. Then they are separated and deposited.
Some flowers can be obtained by rooting leaf pieces such as streptocarpus and sansevieria. 1/3 of the veined leaf is buried in a wet substrate.
Plant propagation by layering
Layers are rooted in ampelous and curly flowers with long shoots. The method is vegetative. Its peculiarity is that the formation of a new plant occurs without separation from the main one. The long shoot is pressed against the nutrient soil with a wire loop or hairpin. Roots appear in this place. When they are already strong enough, you can separate the stem and plant it in a separate container.

Reproduction of flowers by offspring
The method is used for bulbs and cacti. The offspring is an independent daughter plant formed by the mother. After waiting for the offspring to become sufficiently developed, it is cut off or carefully separated. Its own root processes should already form on it. Each is individually planted in a substrate of a suitable type and composition.
Bulbous species also form offspring along with a tiny bulb. When they grow up a little, they are planted in pots. Such plants will bloom in 1-2 years.

Reproduction by children
Children reproduce Kalanchoe tube flowers and Degremona, Bryophillum Degremona. The peculiarity of these plants is that tiny “babies” with independent roots grow on the edges of the leaves. For the purpose of reproduction, they are pinched off using tweezers or fingers, without injuring the root filaments. Placed in a separate container for growing, and then in a flowerpot.

Mustache flower propagation
The whiskers successfully propagate chlorophytum, episcia, tolmia and braided saxifrage, capable of forming small daughter processes with roots at the edge of the stems. They are carefully separated and placed in a pot. Shoots without roots still go through the rooting period.

Division method
The division of the main bush is used for arrowroot, violet, calathea. In these flowers, daughter rosettes are formed near the stem, which can be planted separately. The procedure is carried out in spring or early summer, when the plants have an active vegetation.
For reproduction by division, the mother plant must be removed from the pot. The earthen lump is cleaned around the edges, and the bush is broken or carefully cut with a sharp knife, dividing the mother and daughter parts between them.
The young appendix already has its own growth point and a root system has been formed. The separated plants are planted in pots and placed in the shade. Until complete rooting and the emergence of a new shoot, the soil should always be moist.

Use of spores for reproduction
Ferns most often reproduce by spores. For beginner growers, it can be difficult to implement.
Under good conditions, spores form on the underside of the fern leaves, which are used for reproduction.

For growing spores, a substrate is prepared from peat soil and a small volume of crushed brick chips. The mixture is filled into a flat container with drainage holes, leveled and tamped. Spores are evenly spread over the surface. After that, cover with glass or foil. The container should be placed in a pallet filled with soft rain or melt water. keep in a shaded, warm place for about a month. New shoots can be expected after 4-5 weeks.
The shelter is removed after 2 months. Fortified rosettes dive into containers with cells or small pots.
Seed reproduction
Houseplants are rarely propagated by seed because it is troublesome. The advantage of planting a flower with seeds is that it can get a new shape or color. Varietal characteristics may be lost.
Seeds with fast germination are planted in the ground in March-April, which germinate for a long time - in February. Planting material covered with a dense film should be soaked for 1-2 days in warm water. A quicker way is to sprinkle with hot water. seed treatment with aloe juice or a special preparation will help accelerate germination and flowering.
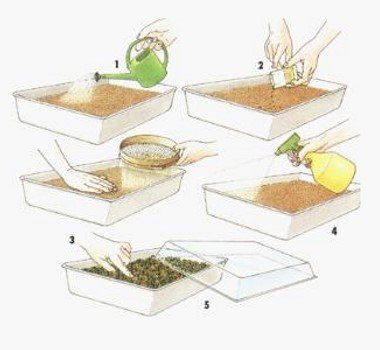
The seeds are sown in the ground heated in the oven for sterilization. The soil consists of peat and sand in equal parts, or it is the soil for seedlings from a store. The container is filled with substrate and sealed. The grains are spread over the ground and covered with a small layer of the same soil. The earth only needs to cover the seeds. Plantings are watered from a watering can with a mesh or sprayed. The container is covered with a transparent material and kept under the conditions indicated on the bag.
Maintenance will require regular watering and ventilation. When there are already small shoots, they are rearranged in a warm place, and the film is removed. After 2-3 leaves appear, dive into separate cups. This will enhance the growth of the root system. to remove the sprout from the common container, stick a pencil or pen near the seedling and gently lift it. When transplanting, the stem needs to be buried more in damp ground. Rooting will take place faster if the seedlings are sprayed with phytohormones and kept in greenhouse conditions.
Watch also the video to learn more about flower propagation at home:




